Definitions and History
Telemedicine, also known as telehealth, refers to the delivery of healthcare services virtually using technology. It allows patients and providers to connect remotely, bridging geographical gaps and improving access to care. The concept of telemedicine dates back several decades, but recent advancements in digital communication hardware and software have revolutionized its implementation.
Benefits for Patients and Providers
Telemedicine offers several advantages:
- Efficiency: Patients save time by avoiding commutes and waiting rooms, leading to more efficient appointments.
- Cost Savings: Reduced transportation expenses, parking fees, and lost work hours contribute to financial benefits.
- Convenience: Patients can schedule appointments at their convenience, sometimes even during non-traditional hours.
- Access to Specialists: Telemedicine breaks down geographical barriers, allowing patients to consult with specialists outside their local area.
- Improved Medication Adherence: Regular virtual check-ins enhance patient compliance with treatment plans.
- Reduced Hospital Stays: Faster diagnosis and management plans lead to shorter hospital stays.
Impact on Practices
Telemedicine has transformed healthcare practices:
- Community Hospitals: Telestroke and teleneurology programs enable community hospitals to consult with specialists remotely, improving patient outcomes and promoting health equity.
- Reduced Wait Times: Telehealth minimizes delays from request to diagnosis, benefiting both patients and providers.
Technology and Features Used
Telemedicine relies on various technologies:
- Video Conferencing: Real-time video sessions between patients and providers.
- Mobile Apps: Patients can access telehealth services via smartphones and tablets, in addition to desktops.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Integration with EHR systems ensures seamless communication, documentation, and management of the patient care cycle.
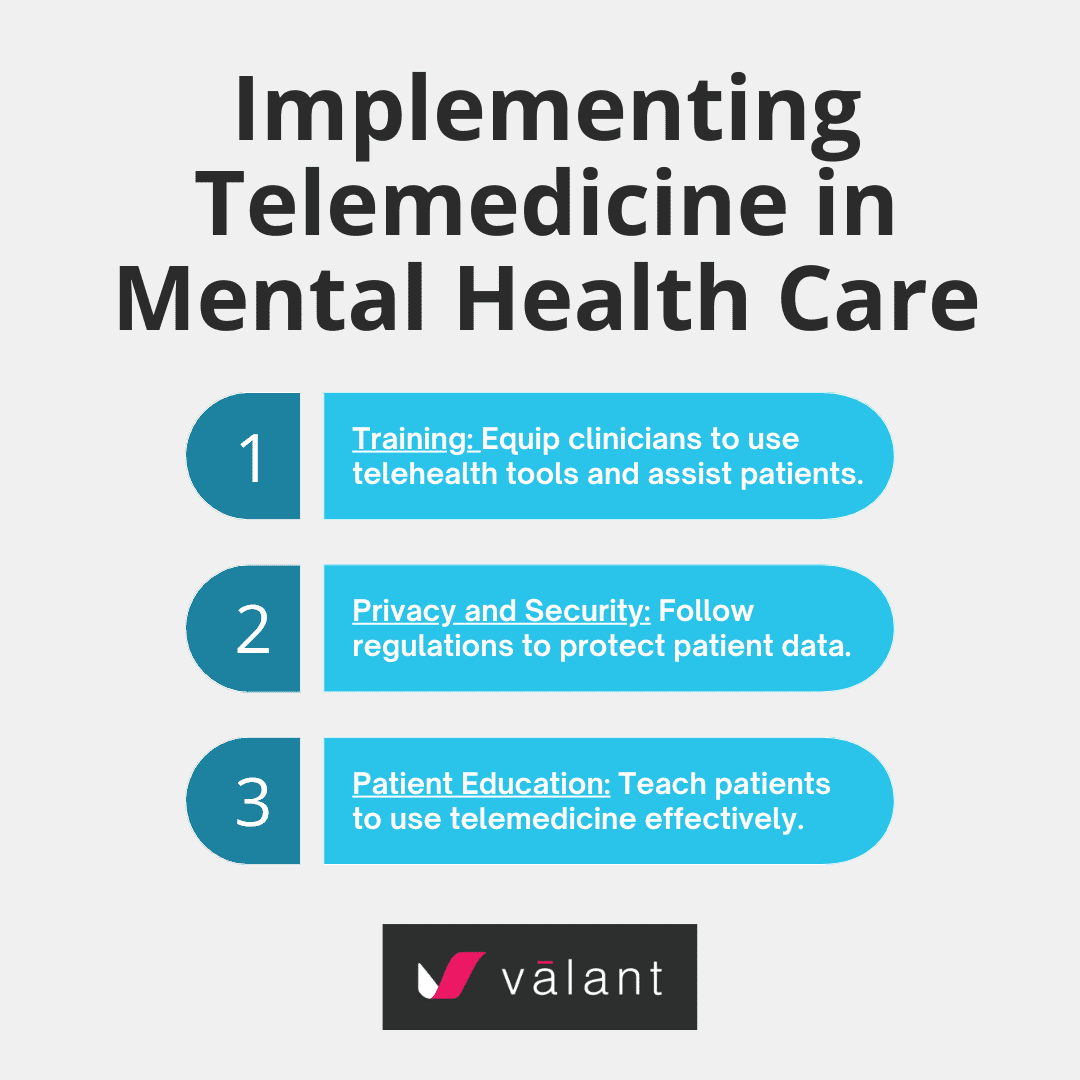
Implementation Strategies
For mental health professionals integrating telemedicine:
- Training: Ensure clinicians are comfortable using telehealth tools and helping their patients do so, as well.
- Privacy and Security: Adhere to privacy regulations (e.g., HIPAA) when handling patient data across systems.
- Patient Education: Educate patients on using telemedicine effectively.
Future Trends
Telemedicine continues to evolve:
- Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and sensors enable continuous health monitoring.
- AI and Chatbots: AI-driven tools assist with triage and basic consultations.
- Expanded Services: Telemedicine will extend beyond primary care to include mental health, chronic disease management, and preventive.
Remember, telemedicine is not just about dollars and cents—it’s about improving patient experiences, enhancing access, and transforming healthcare delivery. As mental health professionals explore telemedicine, they’ll find a wealth of opportunities to provide high-quality care in a digital age.
Starting Your New Practice
Private Practice Business Plan Template
Learn the benefits of developing a private practice business plan and download a free template.